ID : 5213
Position Data Handled by 4-Axis Robots
Position data refers to a set of data which includes RX, RY and five components of base coordinates (the work coordinates system if an work coordinates system is defined). Of these five components, three are robot flange center coordinates (the end-effector tip coordinates if an end-effector is defined) and two are current robot attitude components, as shown below.
Position data allows you to represent the current position of the robot flange center and object points.
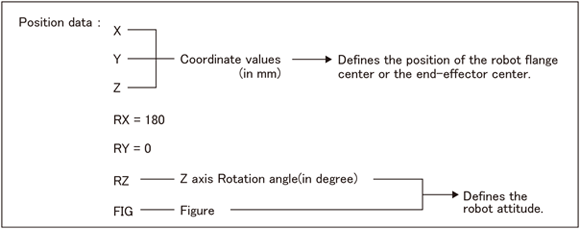
A set of X, Y, and Z coordinate values represents the position of the robot flange center (or tip of the end-effector if defined) expressed in base coordinates (the work coordinates system if an work coordinates system is defined) in units of mm.
The rotation angle expressed by RZ refers to an angle formed by the X axis of the mechanical interface coodinates (or tool coordinates if it is defined) and the X axis of the base coordinates (the work coordinates system if an work coordinates system is defined). The angle is expressed in units of degree. The X-axis of the base coordinate system (or the work coordinate system when it is enabled) that rotates around Z-axis of the base coordinate system corresponds to the X-axis of the mechanical interface coordinate system.
Figure represented by FIG value refers to a figure of robot arm joints. You can not only select a given value, but use the Automatic figure selection function. By using this function, a robot controller automatically selects an appropriate value. For details, refer to "Automatic Figure Selection Function (Auto Fig)".
Figures of 4-Axis Robots
The 4-axis robot can take two types of shoulder figurers (RIGHTY/LEFTY) for one tool-end position.
Combining these two shoulder figures and two types of 4th-axis figure (SINGLE/DOUBLE), a 4-axis robot takes 4 figures for one tool-end position.
| Value | Figures |
|---|---|
| 0 | SINGLE―RIGHTY |
| 1 | SINGLE―LEFTY |
| 16 | DOUBLE―RIGHTY |
| 17 | DOUBLE―LEFTY |
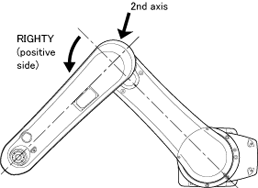
LEFTY ⁄ RIGHTY
| RIGHTY | LEFTY |
|---|---|
 |
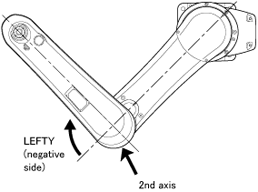 |
When the floor-mounted robot is viewed from the top:
If the 2nd axis is positioned at the positive side on the X axis of the base coordinates the figure is called "RIGHTY"; if at the negative side is called "LEFTY."
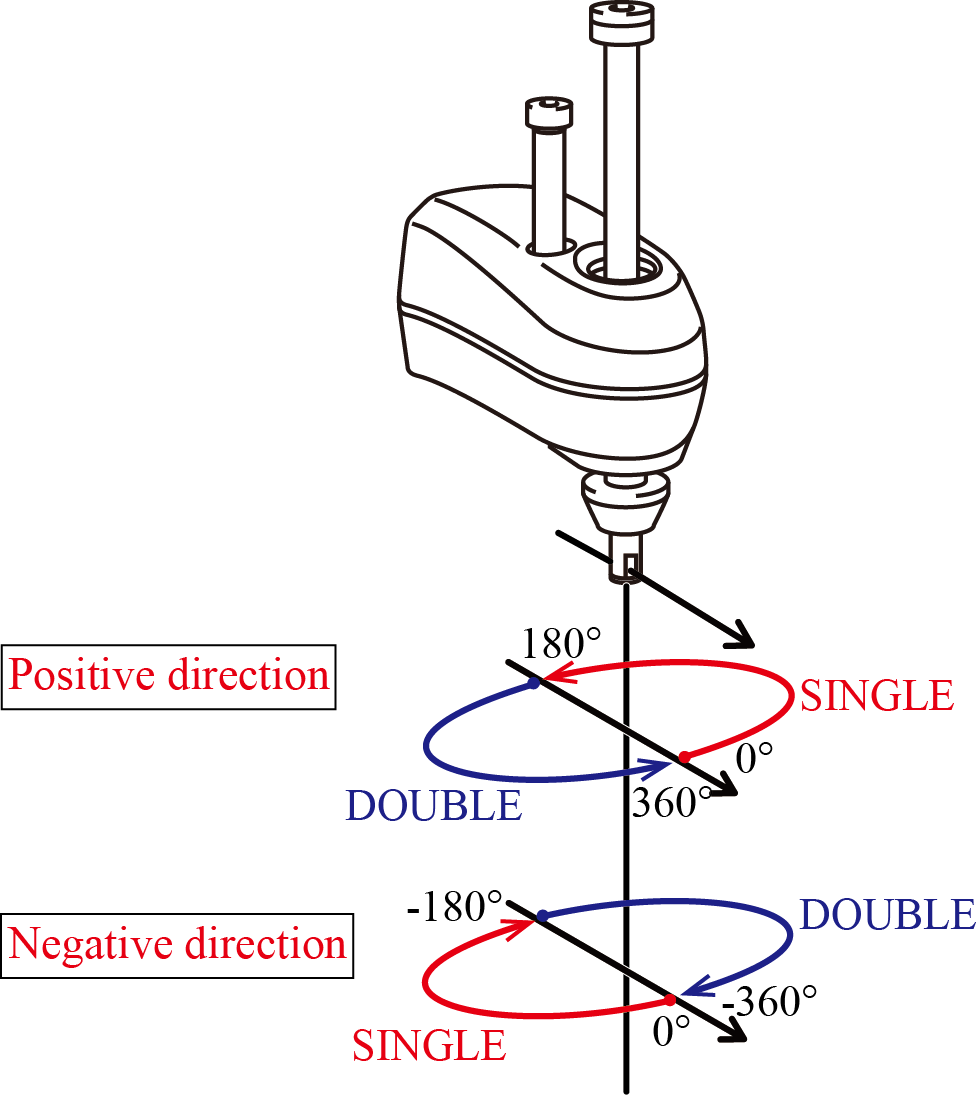
SINGLE ⁄ DOUBLE
If the rotation angle (θ4) of the 4th axis is within the range of -180°<θ4≤180° around the Z axis in mechanical interface coordinates, the figure is SINGLE; if it is within the range of 180°<θ4≤360° or -360°<θ4≤-180°, the figure is DOUBLE.
ID : 5213

