ID : 4870
Overview
Configuration of Extended-Joint Support System
The extended-joint support system is different from the conventional robot system in the following points.
- Robot controller which is equipped with a driver board suited to extended-joint motors to be connected.
- The robot controller and extended-joint motors are connected using extended-joint motor cables, motor conversion cables, encoder cables, and encoder backup batteries (all of these are options).
- Extended-joint motors (option) which are equipped with bus-line encoders. (6-axis robot: up to 2 motors. 4-axis robot: up to 4 motors. motor type selectable)
Models Except UL-Listed Ones
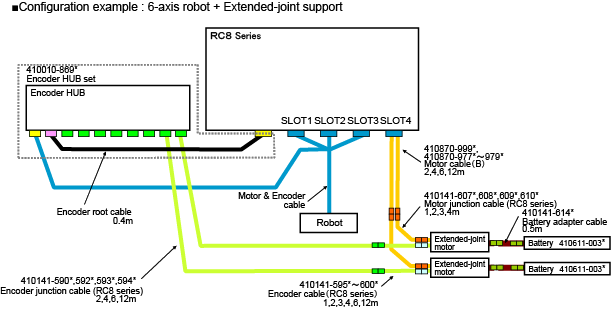
Please refer to this if the figure is not clear. (PDF:214KB)
UL-Listed Model
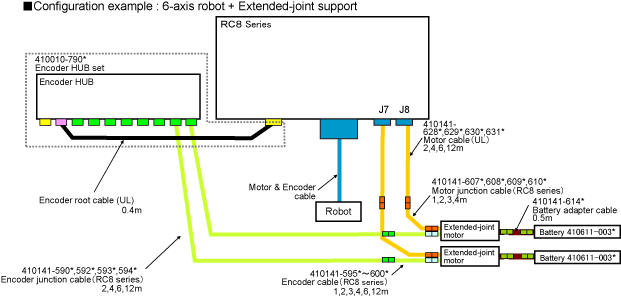
Please refer to this if the figure is not clear. (PDF:243KB)
Extended-Joint Function
The extended-joint function allows you to control extra joints independently of robot joints through the standard interface of the robot controller (RC8 series).
Configuring Extended-Joint Parameters
To use extended-joints, you need to configure the "path configuration parameters" and "servo configuration parameters". The former is for motion definitions (including speed, acceleration, and range of motion); the latter is for setting the gain and others of the extended-joint servo system.
Gain Tuning for Extended-Joints
After setting the motion conditions of extended-joints and checking the motion of the optional mechanism connected to the extended-joint motors, you need to do gain tuning for the servo system. There are the following two types of tuning methods:
- Auto gain tuning
The robot controller performs acceleration/deceleration operation of the extended-joints according to the default pattern preset in the controller. Based on the motion of the extended-joints in that operation, the controller will estimate the inertia of payload and set the appropriate gain automatically. With this method, you can easily do gain tuning of the extended-joint motors. - Manual gain tuning
"Servo Log" monitors the motor speed control value, current motor speed, motor angle deviation, and torque control value. According to the monitored results, you can adjust the gain and torque control filter parameters for optimizing the motion of the extended-joints.
ID : 4870

