ID : 7691
Difference in Robot Motion When Driven in Mechanical Interface Coordinates and Base Coordinates
In Manual mode, if you choose Tool mode and TOOL0 (Flange) on the teach pendant, the robot will run in mechanical interface coordinates. If you choose X-Y mode, WORK0 (Base) will be automatically selected so that the robot will run in base coordinates.
[X], [Y], and [Z] Key Operation
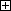
The figure below shows the differences in robot motion when the robot is driven in mechanical interface coordinates and base coordinates, by using the X, Y, and Z keys.
| X-Y mode (in base coordinates) | Tool mode (in mechanical interface coordinates) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| X± | 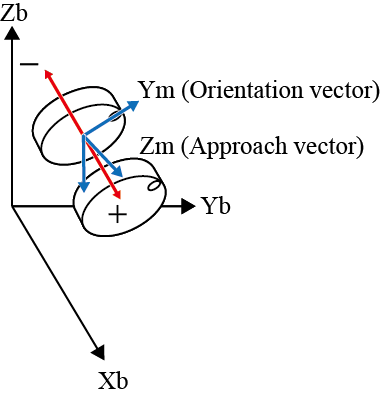 |
X± | 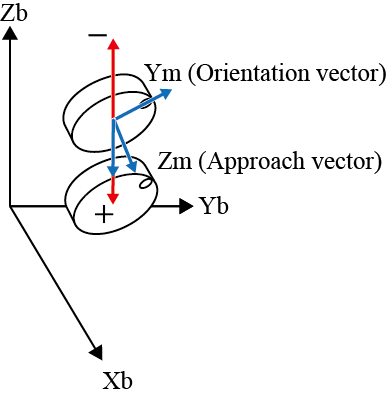 |
| Y± |  |
Y± | 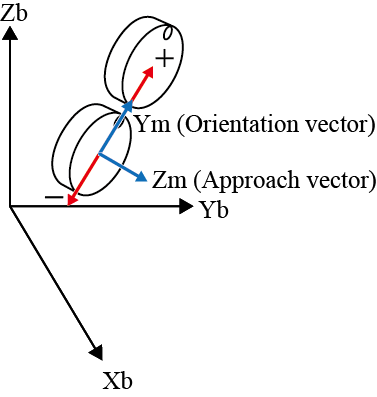 |
| Z± | 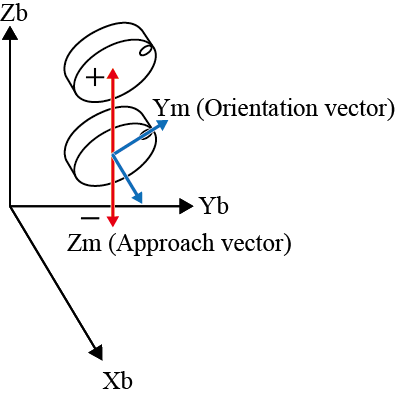 |
Z± | 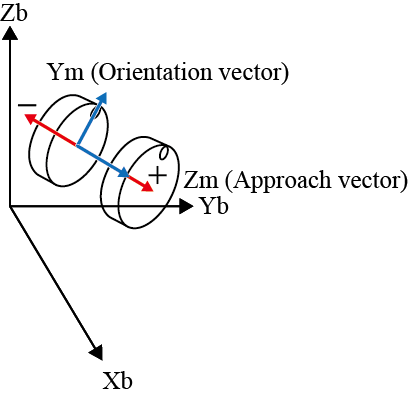 |
[RX], [RY], and [RZ] Key Operation
The figure below shows the differences in robot motion when the robot is driven in mechanical interface coordinates and base coordinates, by using the RX, RY and RZ keys.
| X-Y mode (in base coordinates) | Tool mode (in mechanical interface coordinates) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| RX± | 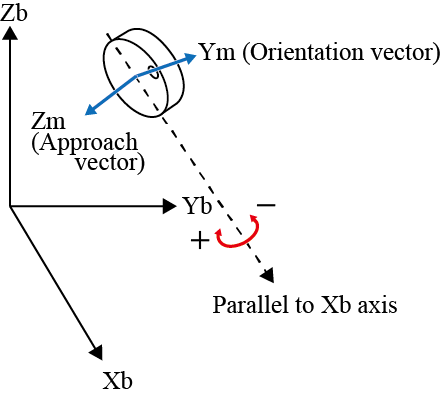 |
RX± | 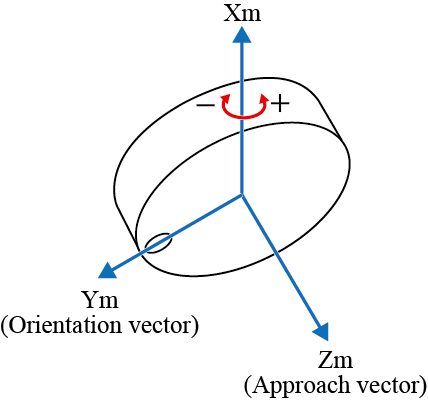 |
| RY± | 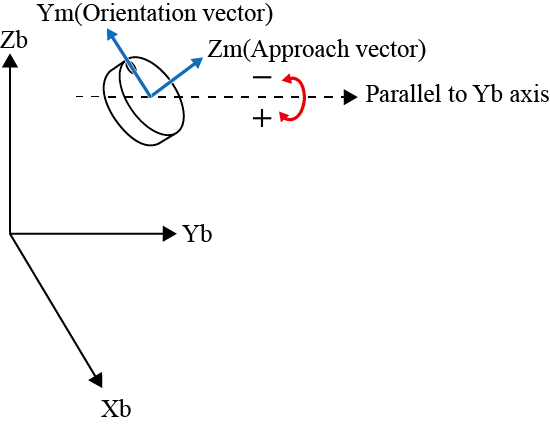 |
RY± | 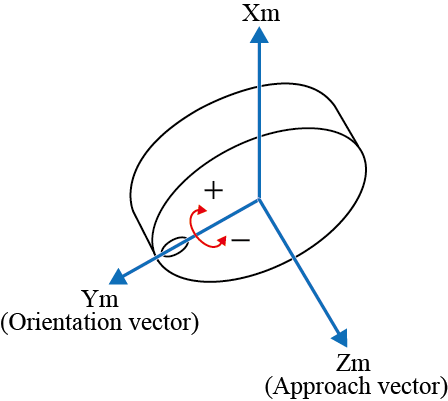 |
| RZ± | 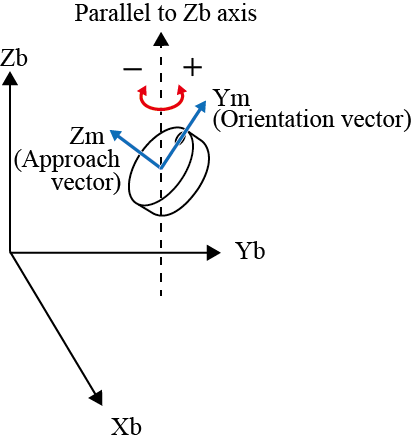 |
RZ± | 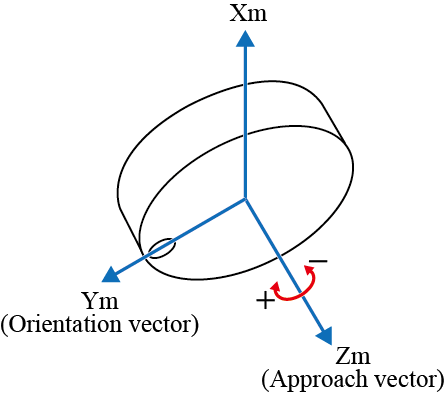 |
The + rotation is for clockwise and the - rotation for counterclockwise with respect to the vector.
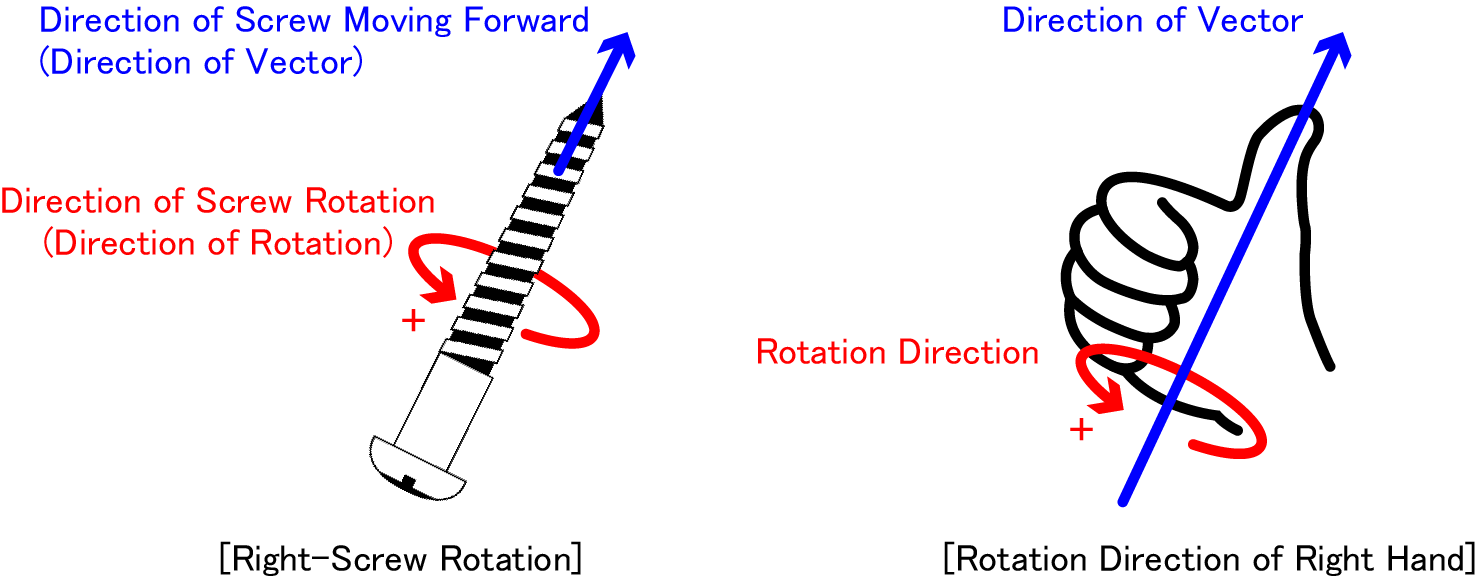
"Clockwise rotation" is based on a principle where a screw can rotate clockwise to screw into a board.In this case, the moving direction of a screw is the vector, and clockwise rotation of a screw is the rotating direction.
"Clockwise rotation" is also called "right hand rotation".In "right hand rotation", the right hand is held with the thumb up.The direction of the thumb is the vector, and the direction of the rest fingers is the rotating direction.
ID : 7691