ID : 5209
Coordinates in 6-Axis Robots
The following three coordinates are available for the 6-Axis robot.
- Base coordinates
- Work coordiantes
- Tool coordinates
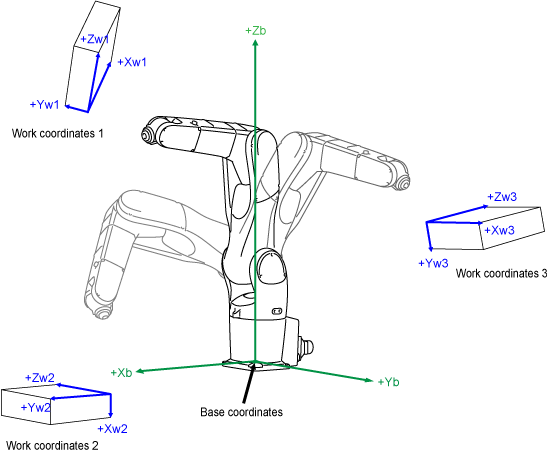
Base Coordinates in 6-Axis Robots
Base coordinates are 3-dimensional Cartesian coordinates with its origin at the center of the robot base. "Base" of the robot is a part where the first axis of the robot is installed.
It has components Xb, Yb, and Zb which are identical with X, Y, and Z in X-Y mode.
Work Coordinates in 6-Axis Robots
Work coordinates are 3-dimensional Cartesian coordinates defined for each operation space of workpiece. The origin can be defined anywhere and as much as needed.
Work coordinates are expressed by the coordinate origin (X, Y, Z) corresponding to the base coordinates and the angles of rotation (RX, RY, RZ) around X, Y and Z axes of base coordinates.
Up to seven work coordinates can be defined and assigned work coordinates #1 to #7.
If work coordinates are not defined, base coordinates go into effect.
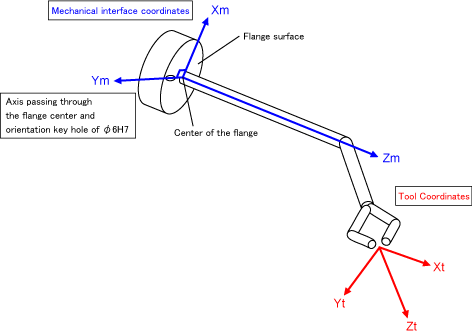
Tool Coordinates in 6-Axis Robots
A tool mounting surface at the end of the robot arm is called a flange. Three-dimensional Cartesian coordinates whose origin at the center of the flange center are called mechanical interface coordinates.
The tool coordinates are 3-dimensional Cartesian coordinates whose origin at the end of the tool mounted on the flange. Based on the origin of the mechanical interface coordinates, the tool coordinates define the offset distance components and axis rotation angles.
The figure below represents VM robots.
For other robot types, the size of orientation key hole is φ5H7.
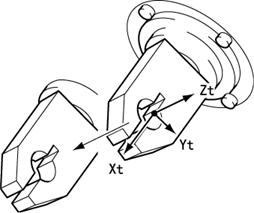
Advantages of Tool Coordinates in 6-Axis Robots
Using tool coordinates in Manual mode allows the tool end to move centering on the point that has been offset in the tool definition.
The table below shows the difference of operations between tool coordinates and mechanical interface coordinates.
| Mechanical interface coordinates(TOOL0) | Tool coordinates |
|---|---|
When X- is pressed
|
When Z- is pressed
Enables you to move the end-effector to your object point in teaching. |
When RX+ is pressed
|
When RZ+ is pressed
Enables you to rotate the end-effector around the Zt axis. |
ID : 5209