ID : 6950
Normal Vector Calculation Function
Overview
Vertical articulated robots are widely used for loading/unloading operations. However, determining a vertical degree against an angled plane by teaching is difficult.
This normal vector calculation function determines the vertical vector against a designated plane by specifying three points on the plane. Setting the calculated vector as an approach vector can save the trouble of teaching the robot figure; as a result, operations on angled planes will be easier.
Description
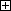
In the figure below, a normal vector is a vector that is normal to the plane A which is composed of V1 and V2. A normal vector can be calculated by cross product of V1 and V2.
To calculate a normal vector, teach three points Position1, Position2 and Position3 as shown below, and then execute NormalVector command. For information about how to use NormalVector command, see NormalVector in the Programmer's Manual.
ID : 6950