ID : 3924
NormalVector
Function
Return a vector which is vertical to a plane where three points belong (normal vector).
Syntax
NormalVector(position1, position2, position3)
Guaranteed Entry
- Position1
- Specify the origin of the vector by position type data, vector type data or homogeneous translation type data. In all data types, elements used for calculation are X, Y and Z.
- Position2
- With Position1, specify a position to determine a vector V1 by position type data, vector type data or homogeneous translation type data. In all data types, elements used for calculation are X, Y and Z.
- Position3
- With Position1, specify a position to determine a vector V2 by position type data, vector type data or homogeneous translation type data. In all data types, elements used for calculation are X, Y and Z.
Return Value
Return a normal vector by vector type data.
Description
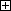
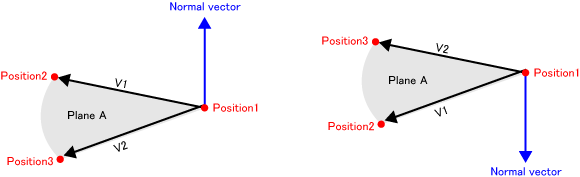
Return a vector which is vertical to a plane where three points belong (normal vector). The direction of the normal vector is the same as the cross product of V1 and V2. See the figure above.
By substituting a normal vector into an approach vector of the target position, you do not need to perform a teaching of a robot figure.For details, refer to the "Normal Vector Calculation Function" of Function Guide. For programming in that case, refer to "Example" shown below.
Related Terms
Attention
Set Position1, 2 and 3 so that the area of the triangle composed by Position1 to 3 becomes as large as possible.
Example
Sub Main
Dim aaa As Trans
'Calculate a normal vector against a plane composed by P10, P11 and P12
V1 = NormalVector (P10, P11, P12)
'Convert the loading position P1 to homogeneous translation type data
aaa = P2T(P1)
'Substitute the normal vector into the approach vector of P1
LetA aaa = V1
'Convert P1 to position type data
P1 = T2P(aaa)
End SubID : 3924